Drip Irrigation in Onsite Wastewater Treatment
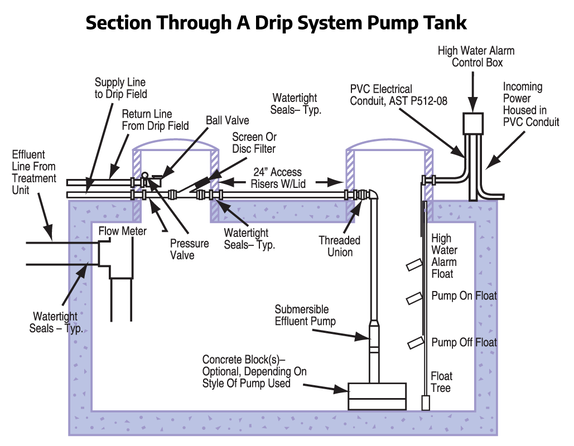
Drip Pump Tank
How does a drip pump tank work?
Once solids have been removed from the sewage and the wastewater (now called effluent) has been treated biologically, then it can flow into the pump tank that contains specialized components. The pump will be equipped with floats to signal water levels in the tank. A control panel, that is typically mounted on the tank or close by on the dwelling, will contain a timer that will manage when the pump runs and for how long.
When the pump is turned on the effluent has to flow through another filter to protect the emitters in the tubing from getting clogged. After the filter, the effluent flows through the tubing system and flows back into the pump tank. A ball valve restricts the return of the effluent returning to the tank creating enough pressure in the tubing to allow the effluent to drip out the emitters. Out of each emitter, effluent will flow at a rate of 1/2 to 1 gallon per hour.
How does a drip pump tank work?
Once solids have been removed from the sewage and the wastewater (now called effluent) has been treated biologically, then it can flow into the pump tank that contains specialized components. The pump will be equipped with floats to signal water levels in the tank. A control panel, that is typically mounted on the tank or close by on the dwelling, will contain a timer that will manage when the pump runs and for how long.
When the pump is turned on the effluent has to flow through another filter to protect the emitters in the tubing from getting clogged. After the filter, the effluent flows through the tubing system and flows back into the pump tank. A ball valve restricts the return of the effluent returning to the tank creating enough pressure in the tubing to allow the effluent to drip out the emitters. Out of each emitter, effluent will flow at a rate of 1/2 to 1 gallon per hour.
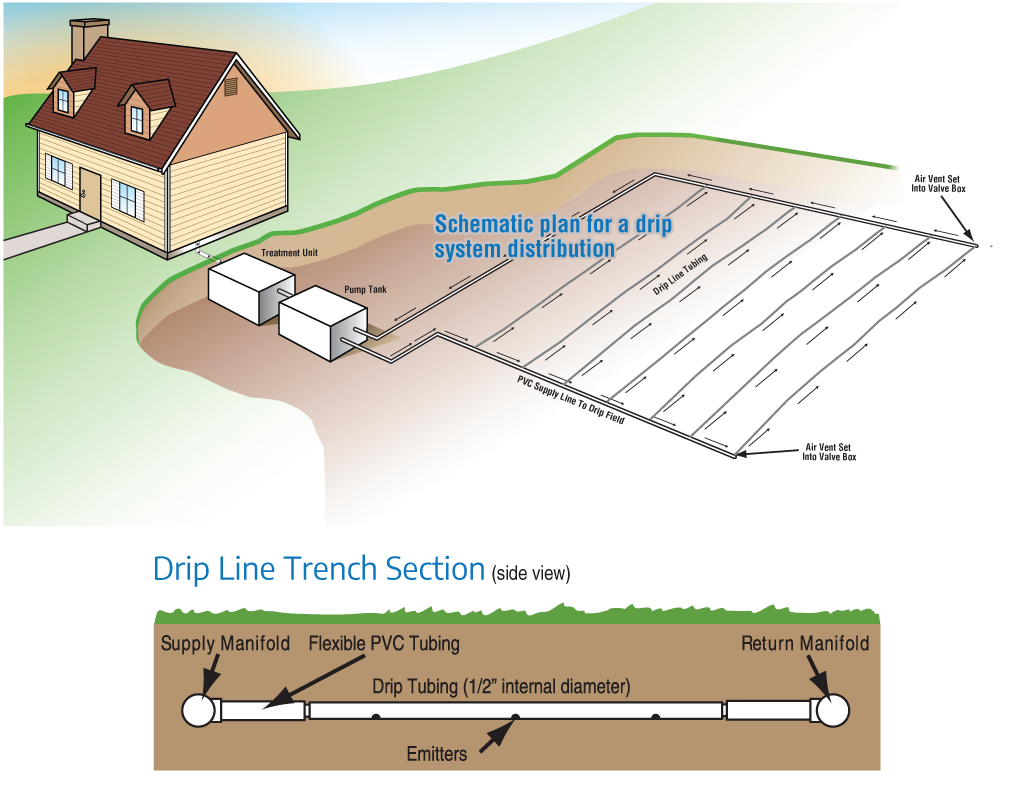
Drip Irrigation System
How does a drip irrigation system work?
Household waste or sewage enters an aeration treatment unit where oxygen is introduced into the waste. This changes the biological process from anaerobic to aerobic. The oxygen speeds up the treatment process and decreases the strength of waste.
This can also be accomplished by using a trickling biofilter. The treated effluent then enters into a pump chamber for distribution to the drip line absorption field.
This process helps assure soils with limitations can then handle the final treatment of the wastewater before it enters the groundwater supply. By treating the wastewater and pumping it in small doses into the soil, many limitations are overcome.
How does a drip irrigation system work?
Household waste or sewage enters an aeration treatment unit where oxygen is introduced into the waste. This changes the biological process from anaerobic to aerobic. The oxygen speeds up the treatment process and decreases the strength of waste.
This can also be accomplished by using a trickling biofilter. The treated effluent then enters into a pump chamber for distribution to the drip line absorption field.
This process helps assure soils with limitations can then handle the final treatment of the wastewater before it enters the groundwater supply. By treating the wastewater and pumping it in small doses into the soil, many limitations are overcome.
Why maintain your system?
The first and most important reason to maintain your system is to protect the health of your family, your community, and the environment. Untreated wastewater from a failing system can contaminate nearby wells, groundwater, and drinking water sources. Once wastewater has polluted the water table, it can become extremely difficult and costly to manage and treat, sometimes at the owners expense.
Significant health risks include hepatitis A, diarrhea, salmonella, giardiasis, tetanus, hookworms, cholera, dysentery, typhoid fever, and staphylococcal infections. Waste water can pollute local water ways with nitrogen and phosphorus.
The second reason is money. Failing systems are expensive to repair and replace, and poor maintenance is a common cause of premature system failure. Routine preventative maintenance costs very little compared to a system replacement. For example a system inspection and maintenance, including pumping the tanks, costs from $150-$300. In contrast, replacing a failing system with a new one typically costs from $4,500 to $30,000, assuming you have enough property to install the replacement system. In addition, property values drop when a system fails.
The third reason is lack of alternatives. A lagoon system was specified for your building location because of some limiting factor(s) in the soil or space constraints. You need to care for the system to keep it operating because there may not be any other legal and healthy ways to handle sewage at your location.
The first and most important reason to maintain your system is to protect the health of your family, your community, and the environment. Untreated wastewater from a failing system can contaminate nearby wells, groundwater, and drinking water sources. Once wastewater has polluted the water table, it can become extremely difficult and costly to manage and treat, sometimes at the owners expense.
Significant health risks include hepatitis A, diarrhea, salmonella, giardiasis, tetanus, hookworms, cholera, dysentery, typhoid fever, and staphylococcal infections. Waste water can pollute local water ways with nitrogen and phosphorus.
The second reason is money. Failing systems are expensive to repair and replace, and poor maintenance is a common cause of premature system failure. Routine preventative maintenance costs very little compared to a system replacement. For example a system inspection and maintenance, including pumping the tanks, costs from $150-$300. In contrast, replacing a failing system with a new one typically costs from $4,500 to $30,000, assuming you have enough property to install the replacement system. In addition, property values drop when a system fails.
The third reason is lack of alternatives. A lagoon system was specified for your building location because of some limiting factor(s) in the soil or space constraints. You need to care for the system to keep it operating because there may not be any other legal and healthy ways to handle sewage at your location.
|
DO's of Maintaining your System
Do obtain necessary permits from the appropriate local agency before doing any construction or repairs.
Do use professional certified installers when needed. Do keep your septic tank accessible for pumping and adjustment. Install risers if necessary. The covers should be locked or of sufficient weight to prevent a child from lifting them. Do have your septic tank inspected annually and tank pumped out every 2-5 years by a professional contractor. Do keep a detailed record of repairs, pumpings, inspections, permits issued and other maintenance activities. Do conserve water to avoid overloading the system. Repair dripping faucets and leaking toilets, avoid long showers and run washing machines and dishwashers only when full. Use water-saving features in faucets, shower heads and toilets. Do divert other sources of water, like roof drains and hillside runoff away from the lagoon system. Use curtain drains, terraces, downspout extensions, retaining walls, etc. to divert water. Do take leftover hazardous household chemicals to an approved hazardous waste collection center for disposal. Use bleach, disinfectants and drain and toilet bowl cleaners sparingly and in accordance with product labels. |
Don'ts of Maintaining your System
Don't go down in a septic tank for any reason. Toxic gases in the tank can be explosive and cause asphyxiation.
Don't allow anyone to drive or park over any part of the system. Don't allow the overflow from the lagoon to leave your property, event during wet weather. A grass cover will not only prevent erosion, but will help dispose of excess water. Don't plant trees or shrubbery near the lagoon. This could cause shading, sludge buildup and increased odor levels. Decaying vegetation can lead to voids in the lagoon berm and promote berm leakage. Don't make or allow repairs to your lagoon system without obtaining the necessary permits. Don't pour into drains any grease, cooking fats, chemical drain openers, paint, varnishes, solvents, fuels, waste oil, photographic solutions, pesticides, pharmaceuticals or other organic chemicals. These materials can upset the bacterial action in the septic tank or lagoon and pollute groundwater. Don't use your toilet for trash as a trash can. Keep out coffee grounds, bones, cigarette butts, disposable diapers, feminine hygiene products, paper towels, facial tissues and other materials that decompose very slowly. Don't add enzyme or yeast additives to the septic tank or lagoon in hopes of improving bacterial action. None have been proven beneficial and some actually cause damage to soil and vegetation and may pollute groundwater. |